Introducción:
As 4-component meningococcal serogroup B vaccine (4CMenB) contains antigens that are present and conserved in non-serogroup B meningococci, cross-reactivity is possible.
Objetivos:
To test the bactericidal effect of 4CMenB vaccination on meningococcal serogroup W (MenW) strains isolated from human samples, with the ultimate aim of understanding the impact that 4CMenB vaccination could have on MenW disease.
Materiales y métodos:
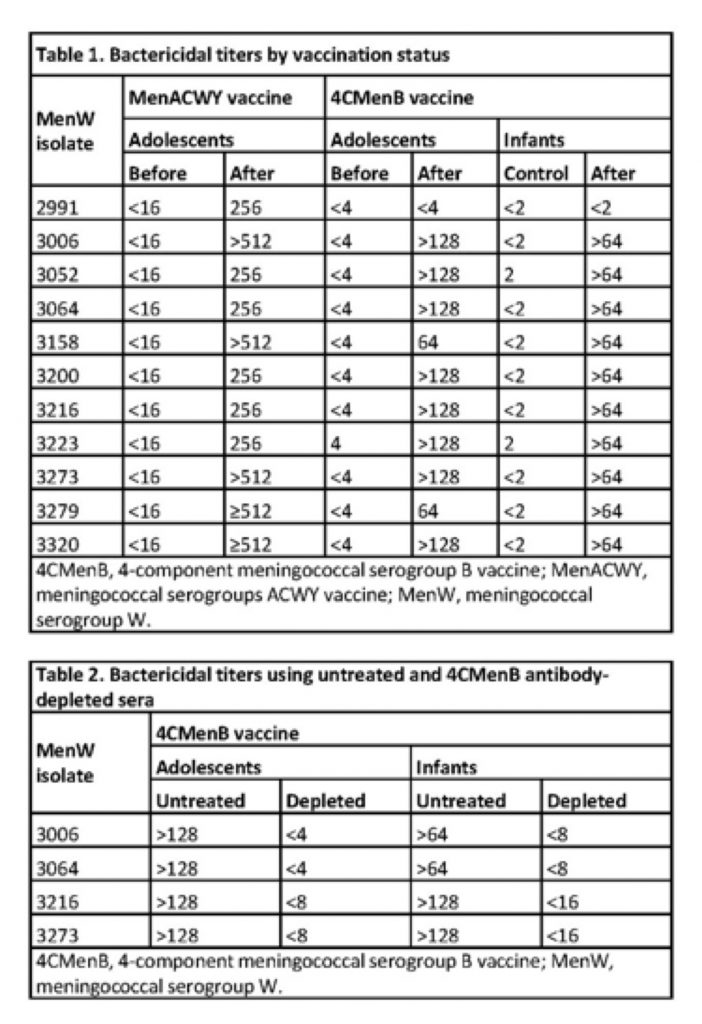
11 MenW isolates considered representative of Argentinian samples from 2010/2011 that were not susceptible to killing by human complement alone were tested in standardized human complement serum bactericidal antibody assays. Three pairs of serum pools were tested, from: adolescents before & after 1 dose of MenACWY (NCT00518180); adolescents before & after 2 doses of 4CMenB (NCT00661713); infants who had not received 4CMenB (NCT00657709) and infants after 4 doses of 4CMenB (NCT00847145). To evaluate whether responses against MenW were due to a specific 4CMenB effect, further tests on 4 isolates used adolescent and infant sera that had been incubated with 500 µg/mL 4CMenB to deplete 4CMenB antibodies. All analyses are descriptive.
Resultados:
The MenW isolates were ST-11 complex/ET-37 complex (n=8), ST-22 complex (n=2), or unknown (n=1). The 3 negative control sera pools elicited titers at or below the minimum dilution tested for all MenW isolates, the post-MenACWY sera elicited titers ≥256 for all MenW isolates, and the post-2-dose 4CMenB adolescent and post-4-dose infant sera elicited titers ≥64 (i.e. highly bactericidal) for 10/11 (91%) isolates (Table 1). When the post-4CMenB sera were depleted of anti-4CMenB antibodies, the titers were reduced to below the minimum dilution tested (Table 2), confirming the specificity of the bactericidal killing.
Discusión / Conclusiones:
4CMenB vaccination has the potential to protect against MenW disease.